|
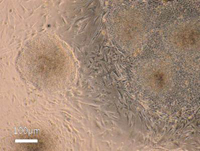
At Sooam, we study embryonic stem cells (ESCs) that are pluripotent, meaning that they have the ability to differentiate into more than 220 cell types found in an adult body. They also exhibit long-term self-renewal, which allows them to reproduce indefinitely. These characteristics make embryonic stem cells a promising tool in gene therapy and regenerative medicine.
Sooam focuses on deriving, growing and differentiating human and animal embryonic stem cells as well as establishing transgenic ES cells.
Publications
Jung, E.M., Son, H.Y., Jeung, M.K., Lee, C.K., Hyun, S.H., Jeung, E.B. Epigenetic signatures of somatic cell nuclear transfer-derived embryonic stem cell. Int. J. Mol. Med. 28: 697-704 (2011).
|
Human embryonic stem cells (ESCs).
Propagation of human ESCs |